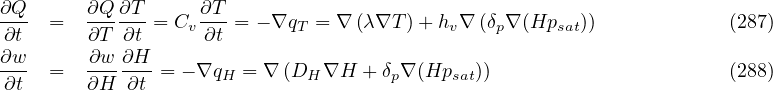
The presented formulation is based on the work of Kuenzel [16]. The model is suitable for problems with dominating water diffusion and negligible water convection. The governing equations for temperature and humidity reads
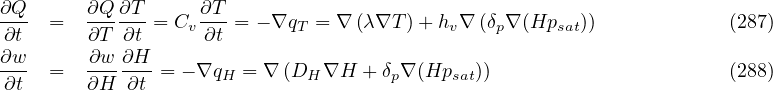
| T | (K) | Temperature |
| H | (-) | Relative humidity 0-1 |
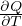 ≈ Cv ≈ Cv | J/K/m3 | Heat storage capacity per volume |
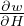 | kg/m3 | Moisture storage capacity - sorption isotherm |
| Q | J/m3 | Total amount of heat in unit volume |
| qT | W/m2 | Heat flux |
| λ | W/m/K | Thermal conductivity |
| hv | J/kg | Evaporation enthalpy of water |
| δp | kg/m/s/Pa | Water vapour permeability |
| psat | Pa | Water vapour saturation pressure |
| w | kg/m3 | Moisture content |
| DH | kg/m/s | Liquid conduction coefficient |
| Dw | m2/s | Water diffusivity |
Numerical solution leads to the system of equations
where
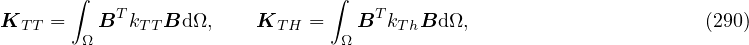
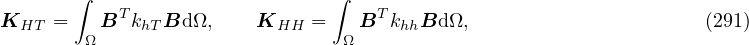
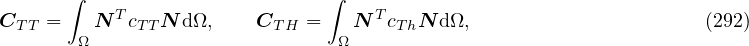
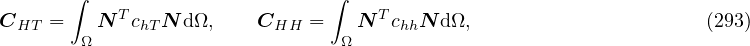
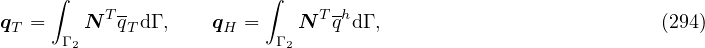
where
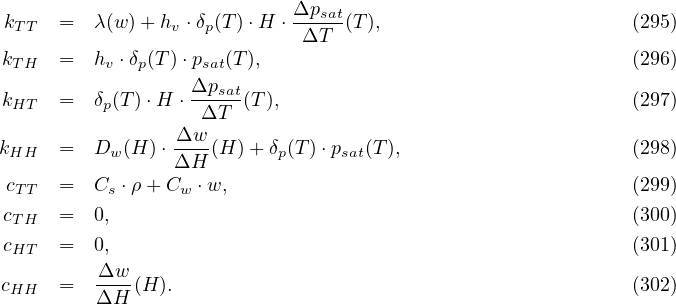
Note, that conductivity matrix K is unsymmetric hence unsymmetric matrix storage needs to be used (smtype).
The model parameters are summarized in Tab. 74.
| Description | Coupled heat and mass transfer material model |
| Record Format | HeMoKunzel num(in) # d(rn) # iso_type(in) # iso_wh(rn) # mu(rn) # permeability_type(in) # A(rn) # lambda0(rn) # b(rn) # cs(rn) # [ pl(rn) #] [ rhoH2O(rn) #] [ cw(rn) #] [ hv(rn) #] |
| Parameters | -num material model number |
| -d bulk density of dry building material [kg/m3] |
|
| -iso_type=0 is isotherm from Hansen needing iso_n, iso_a, =1 is Kunzel which needs iso_b |
|
| -iso_wh maximum adsorbed water content [kg/m3] |
|
| -mu water vapor diffusion resistance [-] |
|
| -permeability_type =0 is Multilin_h needing perm_h, perm_Dw(h), =1 is Multilin_wV needs perm_wV, perm_DwwV, =2 is Kunzelperm needs A as water absorption coefficient [kg/m/s0.5] |
|
| -lambda0rn thermal conductivity [W/m/K] |
|
| -b thermal conductivity supplement [-] |
|
| -cs specific heat capacity of the building material [J/kg/K] |
|
| -[pl] ambient air pressure [Pa], default = 101325 |
|
| -[rhoH2O] water density [kg/m3], default = 1000 |
|
| -[cw] specific heat capacity of liquid water, default = 4183 |
|
| -[hv] latent heat of water phase change [J/kg], default = 2.5e+6 |
|
| Supported modes | _2dHeMo, _3dHeMo |