Parallel 3D three point bending test with nonlocal constitutive model
The 3D three-point-bending notched specimen has been analyzed using direct
explicit integration. The specimen geometry is shown in Fig.
1. and used constitutive model is nonlocal variant of rotating
crack model with transition to scalar damage. The constitutive properties
are summarized in table 1. In order to simulate
static loading, the specimen loading has been controlled by prescribed
displacement of transverse edge on top specimen surface "w = 0.5*0.001*(3.0-t/0.02)*(t/0.02)*(t/0.02)"
(see fig. 1), whose load-time history has been
determined from requirement of minimal inertia forces. Explicit dynamic
computation, 1964 nodes, 9324 linear tetrahedra elements, 7500 time increments.
Nonlocal rotating crack model with transition to scalar damage has been
used. Several parallel platforms were tested, results (real time consumed
and speedups) are available for
IBM SP2, Win NT and Linux clusters.
Some nice pictures from the solution can be foud here.
Speedups:
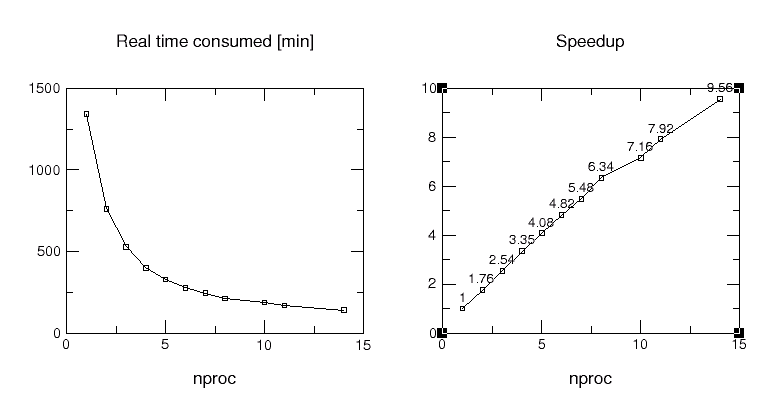
Results on IBM SP2 machine, P2SC processors (120,
160 MHz), HPS (bidirectionally 40 MB/sec).
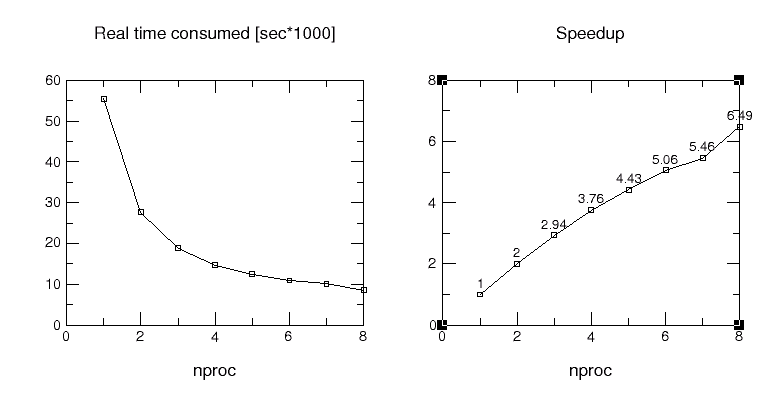
Results for Intel Pentium II Xeon Workstation Cluster
(400 and 450 MHz, Fast Ethernet 100, Win NT Platform, MPI Pro).
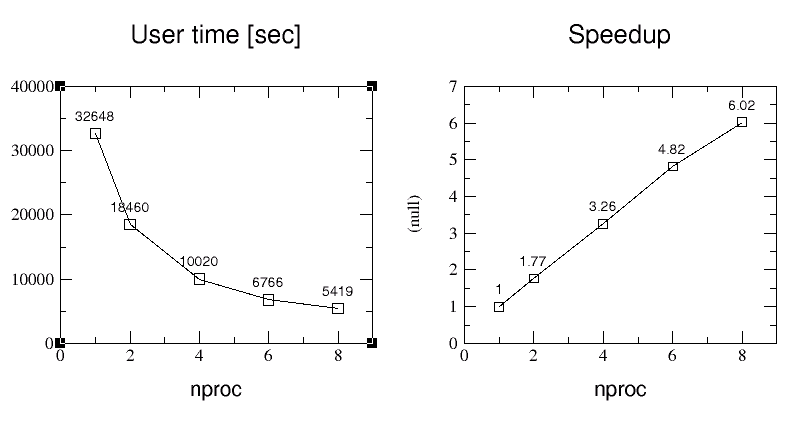
Results for Intel Pentium II Xeon Workstation Cluster
(400 and 450 MHz, Fast Ethernet 100, Linux OS, MPICH).
Constitutive Properties:
| density |
2.5 |
KN/m^3 |
| Young modulus |
20.e3 |
Mpa |
| Poisson coeff |
0.2 |
|
| Tension strength |
2.5 |
Mpa |
| Ultimate tension deformation (when tension stress vanishes) |
0.0005 |
|
| Width of nonlocal averaging zone |
0.025 |
m |
| Shear transition coeff |
0.6 |
|
| Tension stress transition coeff |
0.0 |
|
Table 1: Constitutive properties
References:
- B. Patzák, D. Rypl, and Z. Bittnar.: Explicit parallel dynamics with nonlocal constitutive
models. In B.H.V. Topping and B. Kumar, editors, Developments in Analysis and Design using
Finite Elements Methods. Civil-Comp Press, 1999. ISBN 0 9487 4961 X.



